INDICATIONS AND USAGE
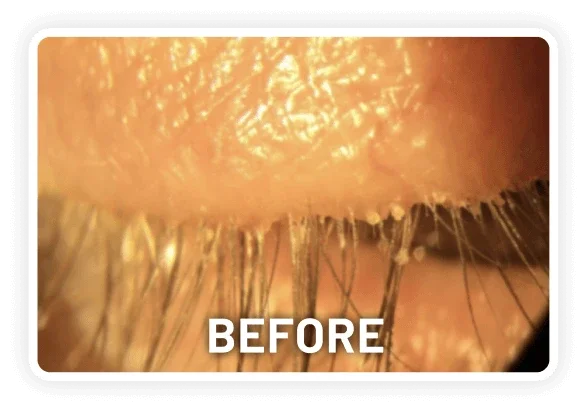
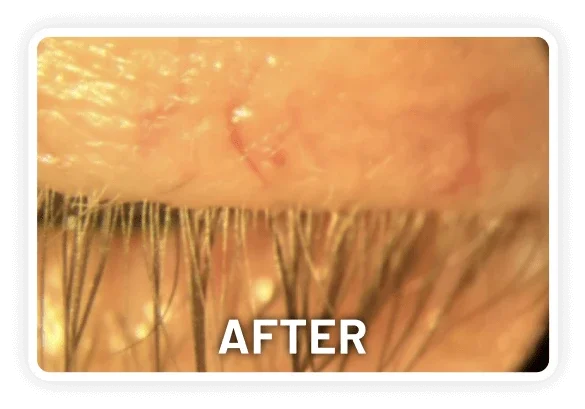
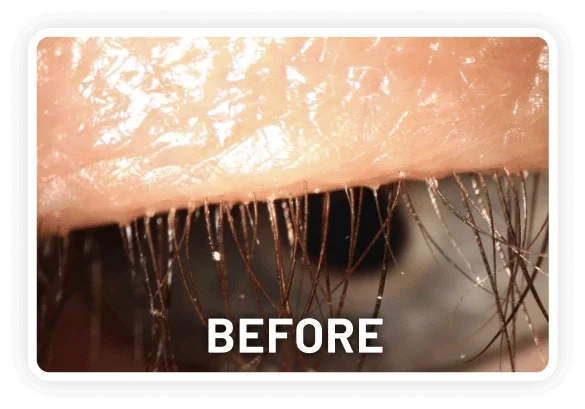
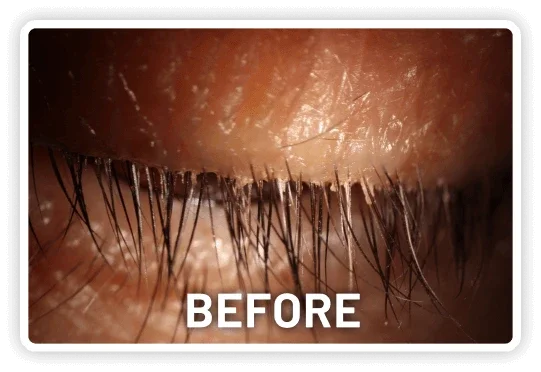
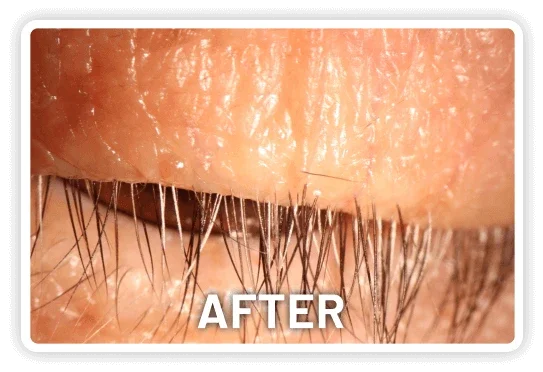
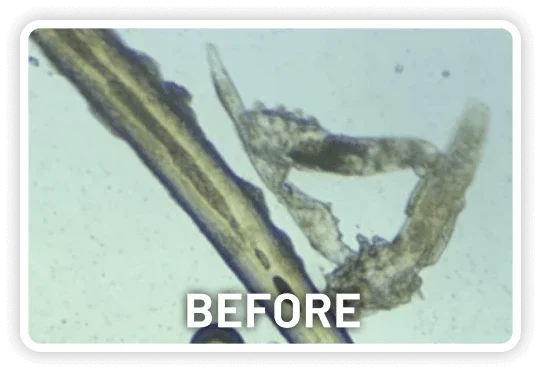
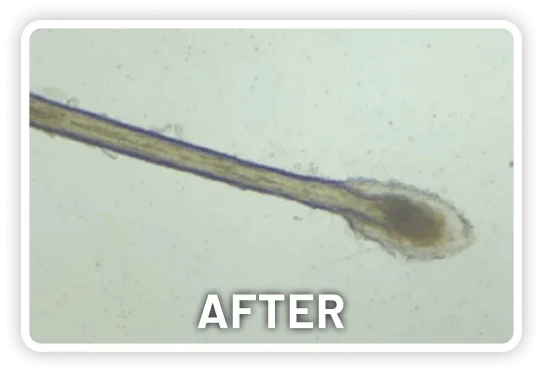
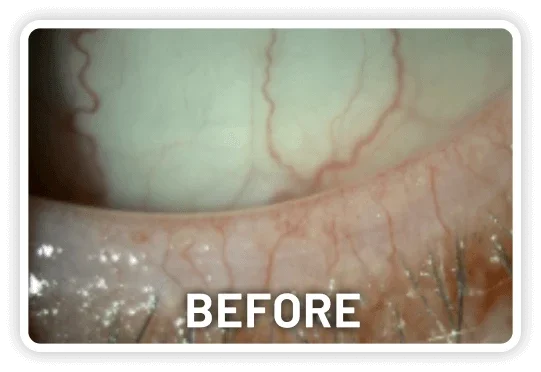
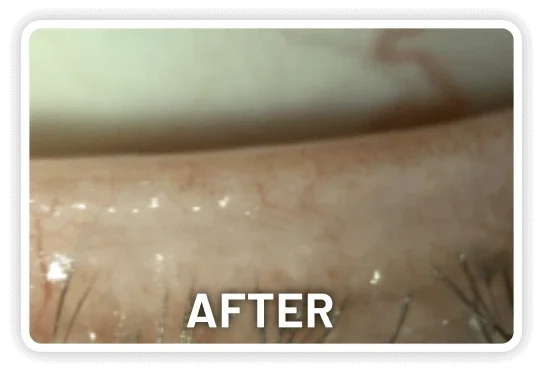
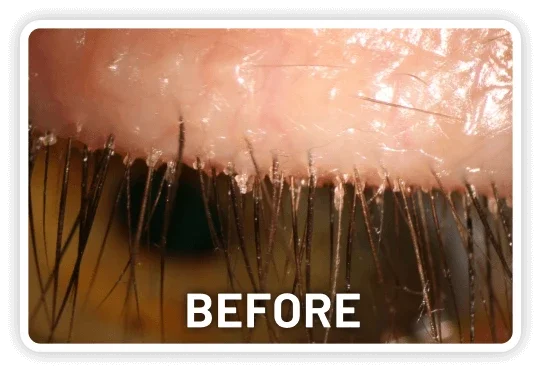
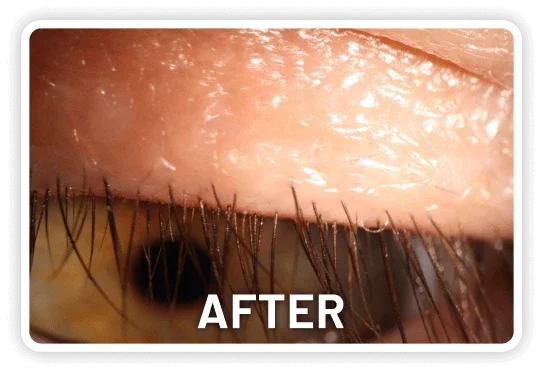
XDEMVY (lotilaner ophthalmic solution) 0.25% is indicated for the treatment of Demodex blepharitis.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION:
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Risk of Contamination: Do not allow the tip of the dispensing container to contact the eye, surrounding structures, fingers, or any other surface in order to minimize contamination of the solution. Serious damage to the eye and subsequent loss of vision may result from using contaminated solutions.
Use with Contact Lenses: XDEMVY contains potassium sorbate, which may discolor soft contact lenses. Contact lenses should be removed prior to instillation of XDEMVY and may be reinserted 15 minutes following its administration.
ADVERSE REACTIONS: The most common adverse reaction with XDEMVY was instillation site stinging and burning which was reported in 10% of patients. Other ocular adverse reactions reported in less than 2% of patients were chalazion/hordeolum and punctate keratitis.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Tarsus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-888-421-4002 or the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 (www.fda.gov/medwatch).
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Available by prescription only.